- UO.1 CMS: Registration
- UO.2 CMS: Management (OS)
- UO.3 CMS: Management (Apps)
- UO.4 Vulnerability Scanning
- UO.5 Penetration Testing
- UO.6 Organizational communication and data flows are mapped
- UO.7 Externals services must be compliant with UO Minimum Security Standards & Controls
- UO.8 Resources (e.g., hardware, devices, data, time, personnel, and software) are prioritized based on their classification
- UO.9 Cybersecurity roles and responsibilities for the entire userbase are established
- UO.10 Cybersecurity roles and responsibilities for the third party stakeholders (e.g., suppliers, customers, partners) are established
- UO.11 The organization’s place in critical infrastructure and its industry sector is identified and communicated
- UO.12 Priorities for organizational mission, objectives, and activities are established and communicated
- UO.13 Privileged users understand their roles and responsibilities
- UO.14 Conduct a Risk Assessment
- UO.15 Physical Security
- UO.16 Wall Jack Access Control
- UO.17 System Hardening
- UO.18 Security Baseline
- UO.19 Security Updates
- UO.20 Application Blocklisting
- UO.21 Anti-malware
- UO.22 Auto-lock screens or consoles
- UO.23 Firewall (Host-based)
- UO.24 Firewall (Network)
- UO.25 Encryption: Data-at-Rest
- UO.26 Encryption: Data-in-Transit
- UO.27 Encryption: Full Disk
- UO.28 User Access Control: Unique Access Account
- UO.29 User Access Control: Least Privilege Access
- UO.30 User Access Control: Access Approval
- UO.31 User Access Control: Authentication
- UO.32 User Access Control: Limit Failed Login Attempts
- UO.33 User Access Control: Inactive Session Timeout
- UO.34 User Access Control: Two-Factor Authentication
- UO.35 User Access Control: Remote Privileged Access Session Security
- UO.36 Web Reputation Filtering
- UO.37 Security and privacy architectures
- UO.38 Power requirements
- UO.39 Remote access is managed
- UO.40 All users are informed and trained
- UO.41 Data is destroyed according to policy
- UO.42 Cybersecurity is included in human resources practices (e.g. personnel screening, deprovisioning)
- UO.43 Identities and credentials are issued, managed, verified, revoked, and audited for authorized devices, users and processes
- UO.44 Incident Response Plan is developed
- UO.45 Logging and Retention
- UO.46 Log Monitoring
- UO.47 File Integrity Monitoring
- UO.48 Incident Recovery: Backup & Recovery
- UO.49 Incident Recovery: Restoration Testing
- UO.50 Determine critically of Information system components
- UO.51 Resiliency requirements will be established based on data classification
- UO.52 Organizational cybersecurity policy is established and communicated
- UO.53 Cyber threat intelligence is received from information sharing forums and sources
- UO.54 Risk management processes are established, managed, and agreed to by organizational stakeholders
- UO.55 Cyber supply chain risk management processes are identified, established, assessed, managed, and agreed to by organizational stakeholders
- UO.56 Separation of system and user functionality
System shall be registered via an ISO approved Configuration Management System (CMS).
Implementation Guidelines:
Register the device(s) with an inventory management system. Responsibility of updates depends on who manages the operating system of the device. For example, Information Services (IS) managed endpoints will be managed by IS.
CMS: Registration systems include MECM, JAMF, and Puppet.
System Operating Systems shall be managed via an ISO approved Configuration Management System (CMS).
Implementation Guidelines:
Register the device(s) with an inventory management system. Responsibility of updates depends on who manages the operating system of the device. For example, Information Services (IS) managed endpoints will be managed by IS.
Implementation Guidelines:
Register the operating system with an inventory management system. The ISO does not dictate which tools are approved, but instead logs tools being currently used and adds them to the in-use tools list after review. This is an ongoing process and this tools list will eventually be listed here.
- 30 days for critical risk vulnerabilities (CVSS 9.0 -10.0)
- 90 days for high risk vulnerabilities (CVSS 7.0 -8.9)
- 120 days for medium risk vulnerabilities (CVSS 4.0 -6.9)
- As time allows for low risk vulnerabilities (CVSS 0.1 -3.9)
Implementation Guidelines:
Enroll the system in the Vulnerability Management Program. Managed systems should already have appropriate agents running for continuous monitoring.
Implementation Guidelines:
Contact the ISO if you’d like to set up a penetration test.
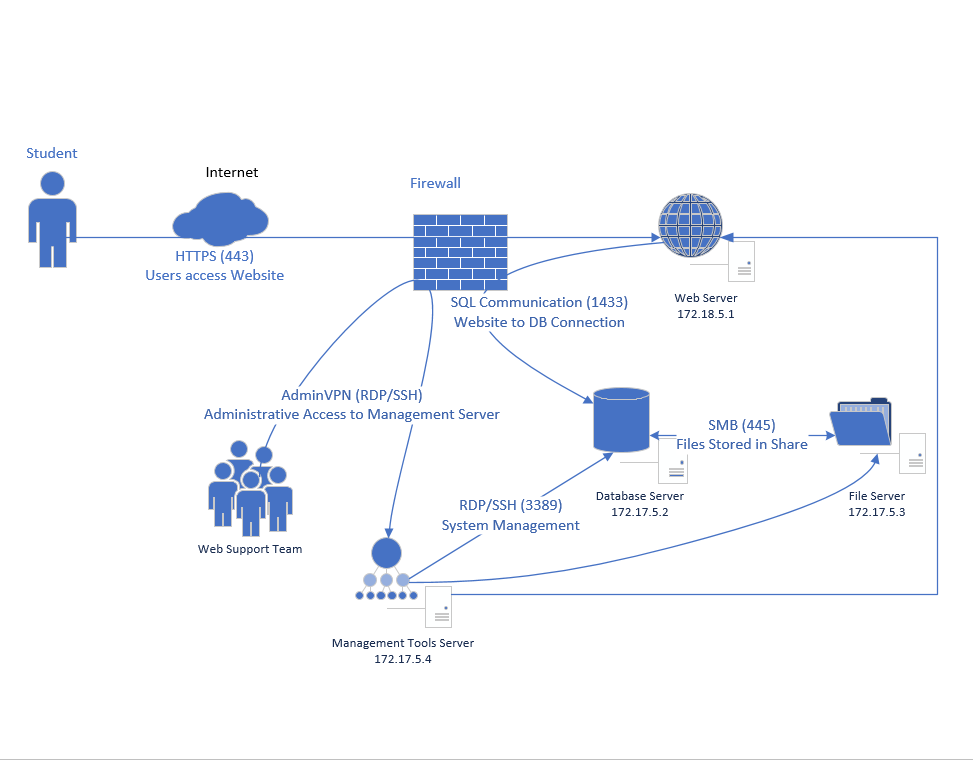
UO.6 Organizational communication and data flows are mapped
Implementation Guidelines:
Draw a diagram. The format and structure of the diagram are secondary to the information it portrays.
Implementation Guidelines:
Understand and document which devices on your system connect to the internet. Reference the Minimum IT Security Controls Standard to ensure those devices are properly configured and secured.
Implementation Guidelines:
System components that contain more sensitive data should be prioritized to receive patches, updates, and extra security measures before components that contain less sensitive data.
Implementation Guidelines:
Make sure that any required cybersecurity roles and responsibilities for staff internal to system are documented and communicated to the Information Security Office.
Implementation Guidelines:
Make sure that any required cybersecurity roles and responsibilities for vendors interfacing with system are documented and communicated to the Information Security Office.
Implementation Guidelines:
Document third party dependencies on the system and designate a point of contact to handle vendor communications.
Implementation Guidelines:
Create a document outlining the system’s mission, objectives, and activities to disseminate to employees.
Implementation Guidelines:
Create a document that outlines responsibilities and expectations for privileged user roles within the system.
UO.14 Conduct a Risk Assessment
Conducting risk assessments includes the following specific tasks:
- Identify threat sources that are relevant to organizations
- Identify threat events that could be produced by those sources
- Identify vulnerabilities within organizations that could be exploited by threat sources through specific threat events and the predisposing conditions that could affect successful exploitation
- Determine the likelihood that the identified threat sources would initiate specific threat events and the likelihood that the threat events would be successful
- Determine the adverse impacts to organizational operations and assets, individuals, other organizations, and the Nation resulting from the exploitation of vulnerabilities by threat sources (through specific threat events)
- Determine information security risks as a combination of likelihood of threat exploitation of vulnerabilities and the impact of such exploitation, including any uncertainties associated with the risk determinations.
Implementation Guidelines:
Follow CISA Guidelines to conduct risk assessment. Reach out to the Information Security Office for further guidance.
Implementation Guidelines:
Place devices behind lockable doors, or in a lockable cabinet when not needed if at all possible. Server devices should be hosted in a UO data center to leverage physical controls.
Implementation Guidelines:
At this time, there is no technical solution for this control. The ISO recommends that walljacks that are not being used aren’t patched to the switch. Advise users with unmanaged systems to connect to the UO wireless network. If a physical network connection is required, work with IT support to ensure documentation of the connection.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends that all systems are configured according to the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Benchmarks for the operating system and applications on a device. Security best practice generally advises the removal or disabling of unnecessary applications, services, and accounts.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends that base operating system images, where available, are obtained from Center for Internet Security (CIS) Hardened Images as a starting point for system configuration.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends systems are configured to automatically update. For Windows systems, this is typically accomplished through MECM. For macOS, this is typically accomplished through JAMF.
UO.20 Application Blocklisting
Application Blocklist shall be used to prevent “known bad” applications from executing.
Implementation Guidelines:
At this time, the UO does not centrally provision tools to achieve this control. This control can be satisfied through antivirus software, Windows AppLocker, or JAMF.
Implementation Guidelines:
Systems that are managed by the Endpoint Device Management (EDM) group, will install Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, regardless of Windows or macOS.
At this time, unmanaged Windows systems may use Microsoft Defender Antivirus (built-in to Windows OS) or McAfee Antivirus downloaded from software.uoregon.edu. For unmanaged macOS devices, download and install McAfee Antivirus from software.uoregon.edu.
Note: McAfee will be deprecated by June 2025; UO Information Services is working to implement Microsoft Defender campus-wide.
Implementation Guidelines:
This OS setting can be managed from the Control Panel in Windows or System Settings on macOS.
Implementation Guidelines:
University-managed devices should have the appropriate antivirus software installed by default, depending on OS.
Data-at-rest (stored) shall be encrypted to ensure confidentiality.
Note: certain combinations of Medium Risk data elements may constitute on aggregate High Risk data.
Implementation Guidelines:
For cloud-based services, the goal is to employ the “trust no one or TNO” principle which requires decryption keys to be accessible only by approved UO personnel, thereby preventing cloud-service vendor personnel or subcontractors from accessing UO data.
UO.25 Encryption: Data-at-Rest
Data-at-rest (stored) shall be encrypted to ensure confidentiality.
Note 1 : certain combinations of Medium Risk data elements may constitute on aggregate High Risk data.
Note 2 : for cloud-based services, the goal is to employ the “trust no one or TNO” principle which requires decryption keys to be accessible only by approved UO personnel, thereby preventing cloud-service vendor personnel or subcontractors from accessing UO data.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
Secure communication protocols include SSH, SCP, sFTP, IPSec, TLS, VPN.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends the usage of BitLocker for Windows, LUKS for Linux systems, and FileVault for macOS.
Implementation Guidelines:
Use DuckIDs for user identification and avoid using shared accounts whenever possible.
UO.29 User Access Control: Least Privilege Access
Least privilege shall be employed to provide the minimum privileges to users and processes.
Implementation Guidelines:
Make sure users and their privileges, especially those with administrative access to devices are documented in some fashion, and make sure that they are trained to only use administrative privileges when necessary to perform a particular business function. On Windows, this procedure looks like using the ‘Run As Administrator’ function when logged in as a user-level account. On MacOS and Linux, this procedure looks like running commands with ‘sudo’ when logged in as a user-level account.
UO.30 User Access Control: Access Approval
Access and privileges shall be authorized by the system owner and reviewed at regular intervals.
Implementation Guidelines:
Make sure users and their privileges are documented in some fashion. This type of document usually looks like a spreadsheet with users on one axis, devices/systems on the other, and either ‘User’ or ‘Admin’ listed for each user’s level of access for each device/system in question. The cadence for account review should be established by the service owner and is recommended to be performed annually and whenever a user is on/offboarded from the system.
UO.31 User Access Control: Authentication
Authentication shall be required for all access to the system.
Implementation Guidelines:
ISO approved authentication sources include one of the following secure/encrypted log-on procedures: Active Directory, LDAP, UO Single Sign-on, external vendor authentication approved by ISO.
Implementation Guidelines:
Most vendor product defaults meet this requirement, but check server-side application settings to ensure this is configured. Operating system settings should be already configured for managed systems, but can be changed in either Control Panel for Windows or System Settings for macOS.
Implementation Guidelines:
Most vendor product defaults meet this requirement, but check server-side application settings to ensure this is configured. Operating system settings should be already configured for managed systems, but can be changed in either Control Panel for Windows or System Settings for macOS.
UO.34 User Access Control: Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication refers to the combination of any two of the following factors:
- something you know(e.g., a password or PIN)
- something you have(e.g., a phone, a token, proximity access card, a digital certificate)
- something you are(e.g., finger print, hand scan, iris scan, etc.)
Implementation Guidelines:
Using UO Cloud datacenter resources for necessary server functionality is recommended by default, and this places server resources behind the university VPN that requires Duo two-factor authentication. Shared resources that sit on the UO network are recommended to be accessed through UO Single Sign On.
UO.35 User Access Control: Remote Privileged Access Session Security
Encrypted communication protocols shall be used for remote privileged access to the system.
Implementation Guidelines:
Do not use outdated and unencrypted protocols such as Telnet.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends following the Minimum Security Controls Standard and understanding the classification level of data present on the system through review of the UO Data Security Classification Table.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is in the process of implementing security training.
UO.41 Data is destroyed according to policy
Data is destroyed according to this standard and in accordance to Data Retention policy.
Implementation Guidelines:
Follow the UO Storage Sanitization Before Reuse, Recycle, or Disposal Procedure.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is in the process of working with HR regarding security of IT assets.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends the review of the UO Data Security Incident Response Policy and the UO Data Security Incident Response Procedure for system stakeholders to understand their incident response responsibilities.
Implementation Guidelines:
Have a backup system for the data. Backups of sensitive data should be encrypted. Backups should be stored remote from the live data. Backups plan should consider recovery time objectives (what is the speed that a restore is needed) and recovery point objectives (how recent does the restorable data need to be). If backups are provided by a hosted service the business agreement with the service should specify the required standards, for UOCloud, Cohesity may meet standards.
Implementation Guidelines:
Contact the ISO for initial configuration and troubleshooting of log forwarding to the ISO SIEM.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Implementation Guidelines:
Document in some fashion the most critical assets of the system, particularly from the perspective of those whose recovery should be prioritized in the case of an incident or outage.
UO.51 Resiliency requirements will be established based on data classification
Data classification (Red, Amber, and Green) accounts for both criticality and sensitivity of data.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends review of the UO Data Security Classification Table in order to understand the applicable classification level for data on the system.
UO.52 Organizational cybersecurity policy is established and communicated
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO provides this service to the University of Oregon.
UO.53 Cyber threat intelligence is received from information sharing forums and sources
Monitoring the websites of your software vendors and reading relevant industry publications for news about emerging threats and available defenses.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
Develop, establish and manage your organization's risk management processes.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO recommends a review of the NIST Risk Management Framework and its seven steps: Prepare, Categorize, Select, Implement, Assess, Authorize, and Monitor. The UO’s Minimum Security Standard outlines the controls that UO systems should allocate to their systems. Please reach out to the ISO for more specific guidance about the RMF process.
UO.55 Cyber supply chain risk management processes are identified, established, assessed, managed, and agreed to by organizational stakeholders
Develop, establish and manage your organization's cyber supply chain risk management processes.
Implementation Guidelines:
The ISO is working on guidance for this control.
UO.56 Separation of system and user functionality
Separate user functionality, including user interface services, from system management.
Implementation Guidelines:
For Windows and macOS: use user accounts (DuckID) for user-level responsibilities and administrative accounts (adm-DuckID) for administrative-level responsibilities.
For Linux: perform tasks with user-level account and use sudo to elevate privileges for administrative functions.